Supply Chain Management

Discover strategies to streamline your supply chain, strengthen supplier relationships, and improve logistics efficiency for business success.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) encompasses the end-to-end planning, coordination, and execution of processes involved in the sourcing, production, and distribution of goods and services. Effective management of the supply chain is critical for businesses to meet customer demands, reduce operational costs, and build a resilient, competitive infrastructure. Below are the core components and advantages of robust logistics and supply chain management:
- Inventory Control: Advanced SCM practices ensure better visibility and control over inventory, minimizing overstock and understock situations. This balance leads to lower carrying costs while maintaining product availability.
- Demand Forecasting: Leveraging data analytics and historical trends, businesses can predict demand accurately. This helps prevent inefficiencies such as overproduction or stockouts essential to streamlined logistics and supply chain management.
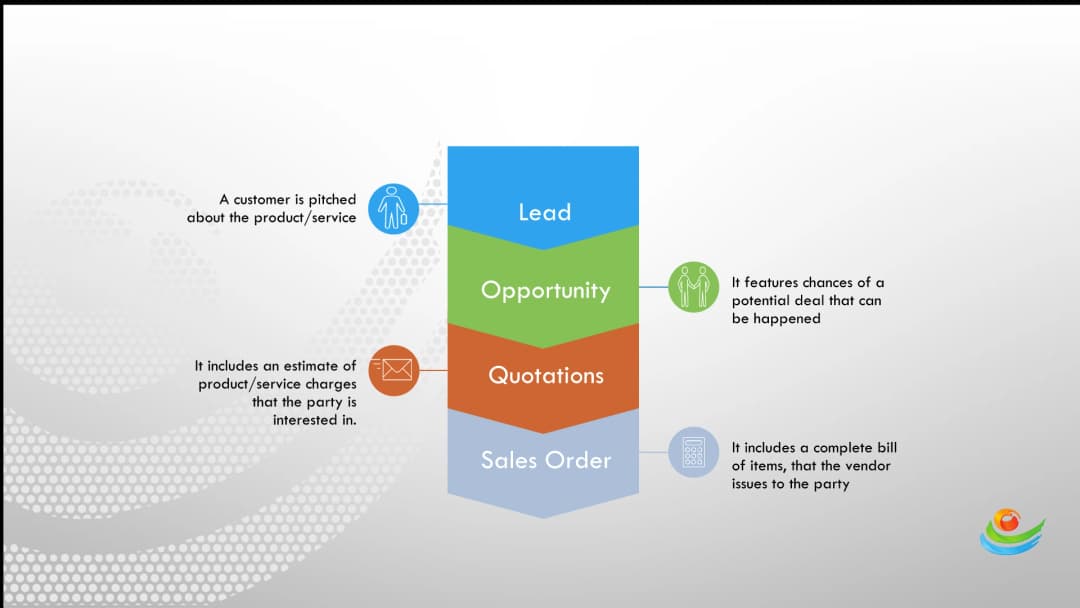
- Supplier Relationship Management: A well-integrated SCM system emphasizes strong supplier relationship management to enhance procurement reliability. Collaborating with trusted vendors ensures timely deliveries, cost optimization, and consistent quality.
- Production Efficiency: SCM improves production workflows by ensuring timely availability of materials and optimal resource allocation. This leads to increased productivity and minimized downtime.
- Cost Reduction: Through improved resource planning, automation, and reduced process redundancies, SCM significantly lowers operational expenses across the supply chain.
- Improved Customer Service: On-time delivery, accurate order fulfilment, and product availability are direct outcomes of effective logistics and supply chain management, fostering stronger customer relationships and loyalty.
- Risk Management: Strategic SCM identifies potential disruptions in supply, quality, or logistics early, enabling proactive risk mitigation and ensuring continuity.
- Global Reach: In a globally connected economy, SCM facilitates smooth cross-border trade, managing logistics, tariffs, compliance, and vendor coordination internationally.
- Environmental Sustainability: Modern supply chains are increasingly optimized for eco-efficiency. SCM contributes to sustainability by minimizing waste, reducing emissions, and optimizing transportation routes.
- Technology Integration: Integration of technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain within SCM enhances real-time tracking, data analytics, and decision-making capabilities across the supply chain network.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: SCM frameworks help businesses align with industry regulations and standards, reducing the risk of penalties and ensuring ethical practices.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Disruptions such as pandemics or geopolitical instability are inevitable. A resilient supply chain built through smart SCM practices can adapt quickly and recover from such challenges effectively.
In conclusion, effective supply chain management backed by robust supplier relationship management and optimized logistics and supply chain processes is pivotal for operational success. It empowers businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, meet compliance, and deliver superior customer value in an increasingly dynamic and competitive global market.